
“Water is the driving force of all nature.” – Leonardo da Vinci
Water is a chemical compound made up of two hydrogen atoms bonded to one oxygen atom. Its chemical formula is H2O. It is a clear, tasteless, and odorless liquid that is essential for all known forms of life. Water is a universal solvent, meaning that it can dissolve many different substances, making it a key component of the Earth’s natural environment. It is also present in the atmosphere in the form of water vapor.
Water is vital for human survival
Water is vital for human survival and is involved in many bodily functions. including digestion, circulation, and the regulation of body temperature. The human body is made up of about 60% water, and it is important to drink enough water to stay hydrated. Water can be found in many different sources. including rivers, lakes, oceans, and underground sources such as wells. It can also be obtained from the food we eat, as many fruits and vegetables contain high amounts of water. Water has many uses, including drinking, cleaning, cooking, and irrigation. It is also used in the production of many products. such as electricity, paper, and clothing. Water is a renewable resource, but it can also be polluted by human activities and can be in short supply in some areas. It is important to use water responsibly and to preserve and protect water sources for future generations.
THE SOURCE OF ALL LIFE
Water is involved in many biological processes. including digestion, circulation, and the regulation of body temperature. The human body is made up of about 60% water, and it is important to drink enough water to stay hydrated. Water is also essential for the growth of crops, and it is used for irrigation in many parts of the world.WATER BIOLOGY
FOUNDATION OF ALL LIFE ON EARTH
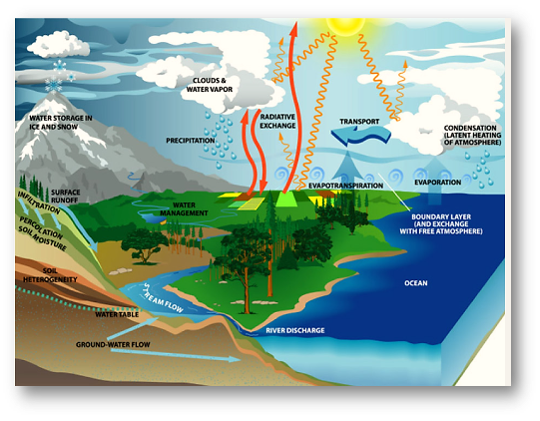
Freshwater is found in rivers, lakes, and underground sources such as wells and aquifers. It is essential for the survival of plants and animals, as well as for human consumption and the production of food. In many parts of the world, access to clean, safe water is a major challenge, and water scarcity is a growing problem. Climate change, population growth, and increasing demands for water for agriculture and industry are contributing to the depletion of freshwater sources in some areas.
Efforts to preserve and protect water resources are important. For ensuring that there is enough clean water for everyone and for the health of the planet. This includes managing water use, protecting natural water sources, and investing in infrastructure and technologies that improve access to clean water. WATER BIOLOGY
HEALTH AND WELL-BEING OF ALL LIVING THINGS
Water can be either contaminated or pure. depending on the presence of contaminants and the level of purity.
Contaminated water is water that has been polluted with substances that make it unsafe for human consumption or other uses. Contaminants can come from a variety of sources, including industrial waste, agricultural chemicals, and untreated sewage. Contaminated water can pose a serious health risk, as it can contain harmful bacteria, viruses, and other pathogens.
There are many different sources of water, both contaminated and pure. Some sources of contaminated water include rivers, lakes, and oceans that have been polluted by human activities or natural events. Sources of pure water include underground aquifers and wells, as well as water treatment plants that purify water from these and other sources. WATER BIOLOGY
It is important to ensure that the water we drink and use is pure and free of contaminants in order to protect our health and the environment.
THE SUBCONTINENT WILL SUFFER THE MOST FROM THE SHORTAGE OF WATER!!!
It is difficult to predict which specific subcontinent will suffer the most from water shortages in the future, as water availability and demand are influenced by many complex factors, including climate, population growth, economic development, and water management practices.
However, it is clear that many parts of the world are already facing water-related challenges, and these challenges are likely to become more acute in the coming years due to factors such as climate change and population growth. Some regions that are particularly vulnerable to water shortages include: WATER BIOLOGY
The Middle East:
Many countries in the Middle East, such as Jordan and Israel, are already facing severe water shortages due to low levels of precipitation and high levels of water demand. These challenges are likely to be exacerbated by climate change, which is expected to lead to more frequent and severe droughts in the region.
Sub-Saharan Africa:
Many countries in Sub-Saharan Africa have limited access to clean, safe water, and water shortages are a major challenge in the region. Drought and overuse of water resources are contributing to the problem, and climate change is expected to make matters worse.
South Asia:
Many parts of South Asia, including India and Pakistan, are facing water shortages due to a combination of high levels of water demand and limited water resources. Poor water management and pollution are also contributing to the problem.
It is important for governments and communities around the world to work together to address water resource challenges and ensure that there is enough clean, safe water for everyone.
ANALYSIS OF WATER RESOURCES WATER BIOLOGY
There are many statistics that can be used to analyze the availability, use, and management of water resources around the world. Some examples include:
Water availability:
This refers to the amount of water that is available for use in a given area. This can be measured in terms of total volume or in terms of the number of people per unit of water.
Water usage:
This refers to the amount of water that is consumed or used in a given area. This can include water used for drinking, irrigation, industrial processes, and other purposes.
Water efficiency:
This refers to the amount of water that is used compared to the amount of water that is available. Higher water efficiency means that more water is being used for a given purpose, while lower water efficiency means that less water is being used.
Water conservation:
This refers to efforts to use water efficiently and preserve water resources for future generations. This can include measures such as reducing water waste, using water-saving technologies, and protecting natural water sources.
Water access:
This refers to the availability of clean, safe water for drinking, cooking, and other household uses. In some parts of the world, access to clean water is a major challenge, and improving water access is an important goal.
By analyzing these and other statistics, it is possible to better understand the state of water resources around the world and identify areas where improvements are needed.
WATER RESOURCE PROBLEMS WATER BIOLOGY
There are many factors that can contribute to water resource problems in different countries around the world. Some common issues include:
Water scarcity:
This refers to a shortage of water. Either due to a lack of precipitation or because the water is not being managed effectively. Water scarcity can be a problem in areas with low annual rainfall. As well as in areas where the demand for water exceeds the available supply.
Drought:
Drought is a prolonged period of dryness that can lead to water shortages and crop failures. It can be caused by a variety of factors. Including low levels of precipitation, high temperatures, and overuse of water resources.
Pollution:
Water pollution can occur when contaminants are introduced into water sources, making them unsafe for consumption or other uses. Pollution can come from a variety of sources, including industrial waste, agricultural chemicals, and untreated sewage.
Overuse of water resources:
In some areas, the demand for water exceeds the available supply, leading to the overuse of water resources. This can result in the depletion of aquifers and other underground water sources. As well as the drying up of rivers and lakes.
Climate change:
Climate change is expected to have significant impacts on water resources around the world. Higher temperatures and changing patterns of precipitation are likely to lead to more frequent and severe droughts. As well as more extreme weather events such as floods and hurricanes, which can damage water infrastructure.
It is important for governments and communities to address these and other water resource problems. In order to ensure that there is enough clean, safe water for everyone. This may involve investing in infrastructure, improving water management practices, and protecting natural water sources.
WATER PRESERVATION STRATEGIES FOR THE SAFE FUTURE
There are many strategies that can be used to preserve and protect water resources for the future. Some examples include:
Improving water efficiency:
One way to preserve water is to use it more efficiently. This can be achieved through the use of water-saving technologies. such as low-flow showerheads and drought-resistant plants. As well as by reducing water waste through conservation efforts.
Protecting natural water sources:
Natural water sources, such as rivers, lakes, and aquifers, need to be protected. In order to ensure the long-term availability of clean, safe water. This can be done through measures such as preserving wetlands. Which help filter pollutants and prevent erosion and protect water catchment areas from development and other human activities.
Investing in water infrastructure:
Upgrading and maintaining water infrastructures. such as treatment plants, pipes, and reservoirs, can help ensure that clean water is available to communities. Water resources are managed effectively.
Promoting responsible water use:
Encouraging individuals and businesses to use water responsibly can help reduce demand and preserve water resources. This can be achieved through education campaigns, water conservation regulations, and incentives for water-efficient practices.
Managing water demand:
Proper water resource management can help ensure that the demand for water is balanced with the available supply. This can involve measures such as regulating water use. Setting water prices to reflect the true cost of water, and investing in technologies that help increase water availability.
By implementing these and other strategies. It is possible to preserve and protect water resources for the safe future of all.
BEST ROUTINE FOR WATER INTAKE
The best routine for water intake depends on a variety of factors, including your age, gender, weight, and activity level. It is generally recommended that adults drink at least eight 8-ounce glasses of water per day, which is known as the “8×8 rule” and is equivalent to about 2 liters or half a gallon. This is known as the daily minimum requirement for water intake.
However, the actual amount of water that an individual needs can vary depending on a variety of factors. For example, people who are more active or live in hot, humid environments may need to drink more water to stay hydrated. Similarly, people who are pregnant or breastfeeding may need to increase their water intake to support their additional needs.
It is important to listen to your body’s thirst signals and drink water when you feel thirsty. You can also incorporate other hydrating beverages, such as water-rich fruits and vegetables, into your diet. If you are concerned about your water intake or are experiencing symptoms of dehydration, such as fatigue, dizziness, or dry mouth, it is a good idea to talk to a healthcare provider for personalized recommendations.
WATER IS THE MOST PRECIOUS RESOURCE WE HAVE!!! WATER BIOLOGY
Saving water and not wasting it is important for a number of reasons:
Water is a limited resource:
Water is a vital resource that is essential for all life on Earth, but it is a limited resource. By using water wisely and not wasting it. We can help ensure that there is enough clean, safe water for everyone now and in the future.
Water conservation helps the environment:
Conservation helps protect natural water sources. Such as rivers, lakes, and aquifers. Which are vital for the health of the environment. It also helps reduce the demand for water. Which can help protect natural habitats and reduce the impact of water withdrawal on the environment.
Water conservation can save money:
Using water efficiently can also help save money on water bills and reduce the cost of water treatment and distribution.
There are many simple steps that individuals can take to save water and reduce waste:
save water and reduce waste
Fix leaks:
Fixing leaks in faucets, pipes, and other water-using appliances can help reduce water waste.
Use water-saving technologies:
Installing low-flow showerheads, faucets, and toilet flappers can help reduce water use.
Water plants wisely:
Water plants and lawns in the early morning or late afternoon, when it is cooler, to reduce evaporation. Use a broom instead of a hose to clean driveways and sidewalks.
Don’t let the tap run:
Turn off the tap while brushing your teeth or washing dishes.
Use water-efficient appliances:
When shopping for appliances, look for models with the Water Sense label, which means they are certified to be water-efficient.
By following these and other water-saving tips, we can all do our part to conserve this valuable resource.
KEYWORDS: water, life, essential, health, intake, resource, precious, liquid, healthy, life-saving
REFERENCES:
- Chung, G., Lansey, K., & Bayraksan, G. (2009). Reliable water supply system design under uncertainty. Environmental Modelling & Software, 24(4), 449-462.
- Nescerecka, A., Juhna, T., & Hammes, F. (2018). Identifying the underlying causes of biological instability in a full-scale drinking water supply system. Water research, 135, 11-21.
- Nitivattananon, V., Sadowski, E. C., & Quimpo, R. G. (1996). Optimization of water supply system operation. Journal of water resources planning and management, 122(5), 374-384.
- Sun, F., Chen, J., Tong, Q., & Zeng, S. (2007). Integrated risk assessment and screening analysis of drinking water safety of a conventional water supply system. Water Science and Technology, 56(6), 47-56.


Pingback: THERMAL CONTRACTION AND EXPANSION!! - Life Biologs
Pingback: WATER SAFETY STARTS WITH YOU!! - Life Biologs