Sleep is a natural state of rest that is essential for physical and mental well-being. During sleep, the body and brain are able to rest and repair themselves, which helps to maintain overall health and function. The average adult needs 7-9 hours of sleep per night, although the exact amount of sleep needed can vary based on individual factors such as age, lifestyle, and overall health. Not getting enough sleep can lead to a variety of negative effects, including fatigue, difficulty concentrating, mood changes, and impaired physical performance. There are several factors that can affect sleep quality and duration, including lifestyle habits such as exercise and diet, and environmental factors such as noise and light. Sleeping disorders, such as insomnia and sleep apnea, can also disrupt sleep and lead to chronic sleep deficiency.
There are several things you can do to improve your sleep, including:
- Establishing a consistent sleep schedule
- Creating a relaxing bedtime routine
- Avoiding caffeine, alcohol, and large meals close to bedtime
- Exercising regularly
- Creating a sleep-friendly environment (e.g. keeping the bedroom cool and dark, using a comfortable mattress and pillows)
If you are having difficulty sleeping or are experiencing chronic sleep deficiency, it is important to speak with a healthcare provider to determine the underlying cause and identify potential treatment options.
HOW DO WE SLEEP Sleeping
Sleeping is a natural process that helps the body and mind rest and repair. It is an important part of maintaining physical and mental health. During sleep, the body relaxes and goes into a state of rest, which allows it to repair and regenerate tissues, consolidate memories, and process information.
There are several stages of sleep, and each stage serves a different purpose. The stages of sleep include:
- Non-rapid eye movement (NREM) sleep: This is the first stage of sleep and is characterized by the body becoming relaxed and the mind becoming less alert.
- Rapid eye movement (REM) sleep: This is the second stage of sleep and is characterized by rapid eye movements, increased brain activity, and vivid dreams.
To fall asleep, it is important to create a relaxing bedtime routine and environment. This can include winding down with a book or other calming activity, keeping the bedroom dark and quiet, and setting a consistent sleep schedule. It is also important to practice good sleep hygiene, such as avoiding caffeine and electronics before bedtime and getting regular exercise and exposure to natural light during the day.
If you are having difficulty sleeping, it is important to speak to a healthcare professional for guidance and support. They can help you identify any underlying causes of your sleep issues and recommend appropriate treatment options.
SLEEP CYCLE (Find the Missing Piece to Your Sleep Routine)
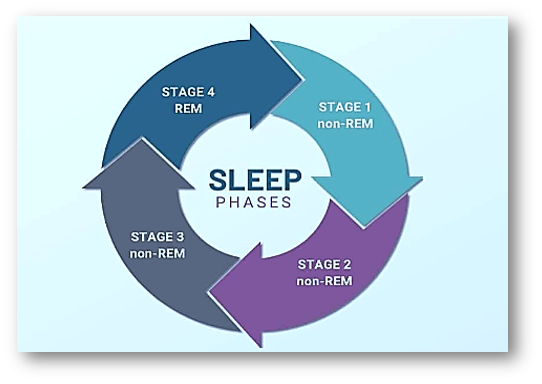
The sleep cycle is the series of changes that occur in the body and brain during sleep. It is divided into two main types of sleep: rapid eye movement (REM) sleep and non-rapid eye movement (NREM) sleep. During a typical night’s sleep, the body goes through several cycles of NREM and REM sleep. Each cycle lasts about 90-110 minutes and typically starts with NREM sleep, followed by a period of REM sleep. During NREM sleep, the body is in a state of rest and repair. Heart rate and breathing slow down, and muscles relax. The brain also exhibits slower, regular brain waves. NREM sleep is further divided into three stages:
Stage 1 NREM sleep: Sleeping
This is the transition stage between wakefulness and sleep. It is a light sleep stage that lasts for about 5-10 minutes.
Stage 2 NREM sleep:
This is a deeper stage of sleep that lasts for about 20-25 minutes. Body temperature and heart rate decrease, and muscle activity slow down.
Stage 3 NREM sleep:
Is the deepest stage of sleep and is also known as slow-wave sleep. It lasts for about 30-40 minutes and is characterized by slow brain waves and a lack of muscle movement.
During REM sleep, the body becomes more active and brain waves become more rapid and irregular. REM sleep is also known as dream sleep, as it is during this stage that most dreams occur. REM sleep typically lasts for about 10-30 minutes and occurs several times throughout the night. The sleep cycle is important because it helps to regulate the body’s sleep-wake cycle and ensure that the body gets the rest it needs to function properly. Dysregulation of the sleep cycle can lead to sleep disorders such as insomnia and sleep apnea.
GET a GOOD NIGHT’S SLEEP, EVERY NIGHT

Here are some sleep tips recommended by healthcare professionals:
- Go to bed and wake up at the same time every day, including on weekends.
- Do activities that help you wind down before bed, such as reading a book or taking a warm bath?
- Keep the room cool, dark, and quiet, and use a comfortable mattress and pillows.
- Avoid activities that can stimulate the brain, such as watching TV or using electronics, for at least an hour before bed.
- Caffeine and alcohol can disrupt sleep, so it is best to avoid them in the hours leading up to bedtime.
- Regular physical activity can improve sleep quality, but avoid vigorous exercise close to bedtime as it may keep you awake.
- A healthy diet can help improve sleep quality. Avoid large meals close to bedtime and try to eat a balanced diet that includes plenty of fruits, vegetables, and whole grains.
- Techniques such as deep breathing, progressive muscle relaxation, or meditation can help to relax the body and mind and prepare for sleep.
- Napping during the day can disrupt your sleep-wake cycle and make it harder to fall asleep at night.
- If you are struggling with sleep despite trying these strategies, consider speaking with a healthcare provider or a sleep specialist to determine the underlying cause and identify potential treatment options.
SOLVE THE PUZZLE OF YOUR SLEEP PROBLEMS
Sleep disorders are conditions that disrupt normal sleep patterns and prevent a person from getting enough restful sleep. Common sleep disorders include:
Insomnia:
Insomnia is difficulty falling or staying asleep, or waking up feeling unrefreshed despite getting enough sleep. It can be caused by a variety of factors, including stress, anxiety, depression, and certain medications.
Sleep apnea:
Sleep apnea is a condition in which a person’s breathing is repeatedly interrupted during sleep. It can lead to daytime sleepiness and an increased risk of heart disease and other health problems.
Restless leg syndrome:
Restless leg syndrome is a condition in which a person experiences an irresistible urge to move their legs, often accompanied by uncomfortable sensations, while trying to sleep.
Narcolepsy:
Narcolepsy is a neurological disorder characterized by excessive daytime sleepiness and sudden attacks of sleep.
Night terrors:
Night terrors are a type of sleep disorder that causes a person to wake up in a state of extreme fear or panic during the night.
Sleepwalking:
Sleepwalking is a type of sleep disorder that causes a person to get up and walk around during the night while still being asleep.
Treatment for sleep disorders may include lifestyle changes, such as establishing a consistent sleep schedule and creating a sleep-friendly environment, as well as medications and/or therapy. It is important to speak with a healthcare provider if you are experiencing difficulty sleeping or excessive sleepiness, as untreated sleep disorders can have serious consequences on physical and mental health.
HEALTHY SLEEP HABITS LEAD TO A HEALTHIER, HAPPIER YOU
There is a strong relationship between diet and sleep. A healthy diet can help improve sleep quality and duration, while an unhealthy diet may contribute to sleep problems.
Eating a diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains can provide the nutrients and energy needed to support good sleep. These types of foods can also help to regulate the body’s natural sleep-wake cycle, as they contain compounds such as melatonin that help to regulate sleep.
In contrast, a diet high in processed and sugary foods can disrupt sleep. Foods and drinks that contain caffeine, such as coffee and soda, can interfere with sleep by stimulating the brain and making it harder to fall asleep. Alcohol can also disrupt sleep, as it can interfere with the body’s natural sleep-wake cycle and lead to disrupted sleep patterns.
Eating large meals close to bedtime can also disrupt sleep, as the body may be too busy digesting food to rest properly. It is generally recommended to avoid eating a heavy meal within a few hours of bedtime.
Overall, a healthy diet that includes a variety of nutrient-rich foods can support good sleep and promote overall health and well-being. If you are having difficulty sleeping, it may be worth considering making changes to your diet and eating habits as part of a holistic approach to improving your sleep.
TAKE CONTROL OF YOUR SLEEP AND IMPROVE YOUR QUALITY OF LIFE
There is a strong relationship between sleep and mental health. Adequate sleep is essential for maintaining good mental health, as it helps to support brain function and regulate mood.
On the other hand, sleep deficiency or sleep disorders can have negative effects on mental health. Chronic sleep deprivation can increase the risk of developing mental health problems such as anxiety, depression, and mood disorders.
Sleep and mental health also tend to influence each other. Poor sleep can contribute to the development or worsening of mental health problems, while mental health problems can disrupt sleep. For example, anxiety and stress can make it difficult to fall asleep or stay asleep, while insomnia can increase the risk of developing anxiety or depression.
It is important to prioritize good sleep hygiene and address any sleep problems in order to maintain good mental health. This may involve making lifestyle changes, such as establishing a consistent sleep schedule and creating a sleep-friendly environment, and/or seeking treatment for sleep disorders or underlying mental health conditions.
WAKE UP FEELING REFRESHED WITH A HEALTHY SLEEP ROUTINE
Here are some tips for establishing a healthy sleep routine:
Set a consistent bedtime and wake-up time:
Go to bed and wake up at the same time every day, including on weekends.
Create a relaxing bedtime routine:
Do activities that help you wind down before bed, such as reading a book or taking a warm bath?
Make your bedroom a sleep-friendly environment:
Keep the room cool, dark, and quiet, and use a comfortable mattress and pillows.
stimulating activities before bedtime:
Avoid activities that can stimulate the brain, such as watching TV or using electronics, for at least an hour before bed.
caffeine and alcohol close to bedtime:
Caffeine and alcohol can disrupt sleep, so it is best to avoid them in the hours leading up to bedtime.
Exercise regularly:
Regular physical activity can improve sleep quality, but avoid vigorous exercise close to bedtime as it may keep you awake.
Eat a healthy diet:
A healthy diet can help improve sleep quality. Avoid large meals close to bedtime and try to eat a balanced diet that includes plenty of fruits, vegetables, and whole grains.
Practice relaxation techniques:
Techniques such as deep breathing, progressive muscle relaxation, or meditation can help to relax the body and mind and prepare for sleep.
Avoid naps: Sleeping
Napping during the day can disrupt your sleep-wake cycle and make it harder to fall asleep at night.
Establishing a consistent and healthy sleep routine can help to improve sleep quality and duration, and promote overall health and well-being. If you are having difficulty sleeping or are experiencing chronic sleep deficiency, it is important to speak with a healthcare provider to determine the underlying cause and identify potential treatment options.
OVERCOME INSOMNIA AND SLEEP PEACEFULLY
Insomnia is a common sleep disorder characterized by difficulty falling or staying asleep, or waking up feeling unrefreshed despite getting enough sleep. Insomnia can be acute (short-term) or chronic (long-term). Chronic insomnia is defined as difficulty falling or staying asleep at least three nights per week for a period of at least three months.
Insomnia can be caused by a variety of factors, including stress, anxiety, depression, and certain medications. It can also be a symptom of an underlying health condition, such as sleep apnea or restless leg syndrome.
Insomnia can have negative effects on physical and mental health, including fatigue, difficulty concentrating, mood changes, and an increased risk of developing other health problems.
Treatment for insomnia may include lifestyle changes, such as establishing a consistent sleep schedule and creating a sleep-friendly environment, as well as medications and/or therapy. It is important to speak with a healthcare provider if you are experiencing difficulty sleeping or are struggling with chronic insomnia, as untreated insomnia can have serious consequences on overall health and well-being.
“A good night’s sleep is within reach, Take the first step towards better sleep today now Sleep soundly and wake up ready to conquer the day”
KEYWORDS: Rest, Nap, Slumber, Snooze, Doze, Catnap, Dream, sleep in,
REFERENCES:
- Ferrara, M., & De Gennaro, L. (2001). How much sleep do we need?. Sleep medicine reviews, 5(2), 155-179.
- Newman, A. B., Nieto, F. J., Guidry, U., Lind, B. K., Redline, S., Shahar, E., … & Quan for the Sleep Heart Health Study Research Group, S. F. (2001). Relation of sleep-disordered breathing to cardiovascular disease risk factors: the Sleep Heart Health Study. American journal of epidemiology, 154(1), 50-59.


Pingback: ANXIETY SYMPTOMS LEAD TO STOMACH UPSET!! - Life Biologs