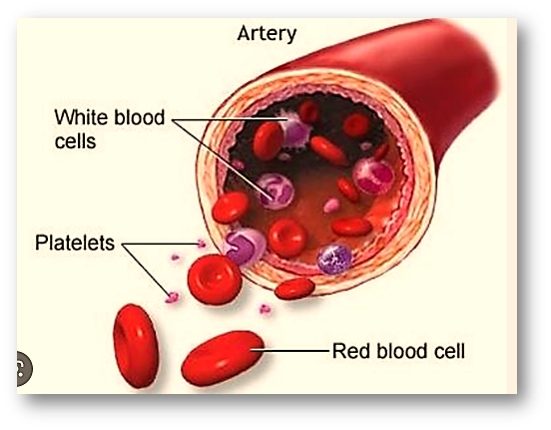
PLATELETS!!
Platelets are small, disc-shaped cells that are a component of blood. They play an important role in blood clotting, helping to stop bleeding when a blood vessel is injured. Platelets are also known as thrombocytes. Low platelet counts can lead to abnormal bleeding and bruising, while high platelet counts can increase the risk of blood clots. Platelet disorders can be caused by a variety of factors, including certain medications, underlying medical conditions, and genetic disorders.
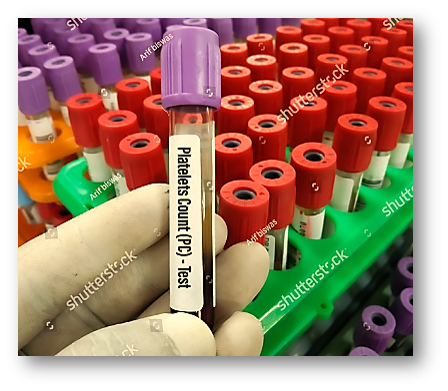
PLATELETS COUNT!!
A platelet count is a measure of the number of platelets in a person’s blood. It is typically measured as part of a complete blood count (CBC), which is a routine blood test used to evaluate overall health. Normal platelet count ranges from 150,000 to 450,000 platelets per microliter of blood. A count below 150,000 is considered low, which is known as thrombocytopenia and it can cause abnormal bleeding and bruising. A count above 450,000 is considered high, which is known as thrombocytosis and it can increase the risk of blood clots. Factors that can cause changes in platelet count include certain medical conditions, medications, and lifestyle factors.
WHAT DO PLATELETS DO IN THE BODY??
Platelets play an important role in the body’s ability to stop bleeding. When a blood vessel is injured, platelets will gather at the site of the injury to form a clot. They do this by sticking together and releasing chemicals that promote clotting. This process helps to prevent the loss of blood by sealing off the injured vessel. Platelets also play a role in the healing process by releasing growth factors that help to repair the damaged tissue. Additionally, platelets have a role in the body’s immune system by releasing molecules that can attract white blood cells to the site of an infection or injury.
NORMAL AND ABNORMAL PLATELETS LEVELS!!
A normal platelet count is typically considered to be between 150,000 and 450,000 platelets per microliter of blood. However, the exact normal range may vary slightly depending on the laboratory that performs the test.
When the platelet count is lower than 150,000 per microliter it is known as thrombocytopenia. This condition can be caused by a variety of factors including medications, infections, and certain medical conditions such as cancer, autoimmune disorders, or bone marrow failure. Low platelet counts can lead to abnormal bleeding and bruising.
When the platelet count is higher than 450,000 per microliter it is known as thrombocytosis. This condition can be caused by certain medical conditions, such as cancer, or by certain medications. High platelet counts can increase the risk of blood clots.
It’s important to note that abnormal platelet counts can be a symptom of an underlying medical condition, and the cause should be determined by a healthcare professional.
SYMPTOMS OF LOW PLATELET COUNT!!
Low platelet counts, also known as thrombocytopenia, can cause a range of symptoms. The severity of symptoms can vary depending on the underlying cause and the degree of platelet deficiency. Common symptoms of low platelet count include:
Bruising easily:
Platelets play a crucial role in blood clotting and help stop bleeding when a blood vessel is injured. When the platelet count is low, the blood does not clot as easily, leading to easy bruising.
Abnormal bleeding:
Low platelet count can cause abnormal bleeding from the gums, nose, or other areas.
Petechiae:
Tiny red or purple dots on the skin are caused by bleeding under the skin.
Fatigue, weakness:
The body may be working harder to try to stop bleeding, which can lead to fatigue and weakness.
Enlarged spleen (splenomegaly):
A low platelet count may cause the spleen to enlarge.
Jaundice:
Yellowing of the skin and whites of the eyes caused by the buildup of bilirubin in the blood.
Anemia:
Low platelet count can lead to anemia, which can cause fatigue, weakness, and shortness of breath.
It’s important to note that some people with low platelet counts may have no symptoms at all. It’s important to consult a healthcare professional for proper diagnosis and management of low platelet count.
HEALTHY EATING INCREASES YOUR PLATELETS LEVEL!!

Eating a diet rich in fruits and vegetables can promote overall health and may help to maintain normal platelet levels. Some fruits and vegetables that are particularly high in vitamins and minerals that are essential for platelet production include:
Papaya:
It contains an enzyme called papain which is known to increase platelet count.
Pomegranate:
It is rich in antioxidants and Vitamin C, which can promote the production of platelets.
Guava:
It is rich in Vitamin C, which is needed for platelet production.
Kiwi:
It is high in Vitamin K and Vitamin C, which are essential for platelet formation.
Berries (strawberries, blueberries, raspberries):
They are rich in antioxidants and Vitamin C.
Spinach:
It is rich in Vitamin K, which is needed for platelet production.
Sweet potatoes:
They are high in Vitamin A, which is needed for platelet formation.
It’s important to note that eating certain fruits and vegetables alone may not significantly increase platelet count in case of thrombocytopenia caused by underlying medical conditions. It’s important to consult a healthcare professional for proper diagnosis and management of the underlying condition.
WHICH DISEASES CAUSE PLATELETS COUNT LOW??
There are many different medical conditions that can cause a low platelet count, also known as thrombocytopenia. Some of the most common causes include:
Bone marrow disorders:
Such as leukemia, aplastic anemia, and myelodysplastic syndrome, which can prevent the bone marrow from producing enough platelets.
Autoimmune disorders: platelet counts
Such as lupus, rheumatoid arthritis, and idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura (ITP), which can cause the body’s immune system to attack and destroy platelets.
Medications:
Heparin, quinine, and certain cancer chemotherapy drugs can cause thrombocytopenia.
Vitamin deficiency:
Such as vitamin B12 and folate deficiency can cause thrombocytopenia.
Infections:
Dengue fever, hepatitis, and HIV can cause a low platelet count due to their ability to damage the bone marrow or cause direct platelet destruction.
Toxins: platelet counts
Exposure to certain toxins such as alcohol, pesticides, and heavy metals can cause thrombocytopenia.
Pregnancy:
Pregnancy-associated thrombocytopenia can occur in some women during pregnancy or postpartum
It’s important to note that a low platelet count can also be a symptom of an underlying medical condition that requires proper diagnosis and management. It’s important to consult a healthcare professional for proper diagnosis and management.
HERBAL REMEDIES FOR RECOVERY OF PLATELETS COUNT!!
Herbal remedies have been traditionally used for recovery of platelet count, however, it’s important to note that most herbs have not been extensively studied for their effectiveness and safety in treating thrombocytopenia. Therefore, it’s important to consult a healthcare professional before taking any herbal remedies.
Some herbs that have traditionally been used to increase platelet count include:
Ginkgo Biloba:
It is known to increase blood flow and improve circulation.
Holy basil: platelet counts
It is known to have anti-inflammatory properties and to help boost immunity.
Turmeric:
It has anti-inflammatory properties and is traditionally used to improve circulation.
Fenugreek:
It has been traditionally used to help increase platelet counts.
Astragalus:
It has been traditionally used to boost the immune system and improve blood circulation.
Neem:
It has traditionally been used to boost the immune system and improve blood circulation.
It’s important to note that it’s not yet clear whether these herbs are effective for increasing platelet count, and more research is needed to confirm their effectiveness and safety. Additionally, some herbs may interact with other medications and can have side effects, so it’s important to consult with a healthcare professional before taking any herbal remedies.
MYTHS ABOUT PLATELETS RECOVERY AND DEFICIENCY!!
There are several myths surrounding platelet recovery and deficiency, some of the most common ones include:
Myth: Eating certain foods can instantly increase platelet count:
While eating a healthy diet that includes fruits and vegetables can promote overall health and may help to maintain normal platelet levels, it is not possible to instantly increase platelet count by consuming certain foods.
Myth: Drinking alcohol can increase platelet count:
Drinking alcohol can actually decrease platelet count and can also lead to other health problems.
Myth: Platelet deficiency is not a serious condition:
Platelet deficiency can be a serious condition, and if left untreated it can lead to abnormal bleeding and bruising, and even cause life-threatening situations.
Myth: Platelet deficiency can be cured with herbal remedies:
While some herbs may have traditional uses for increasing platelet count, it’s not yet clear whether these herbs are effective for increasing platelet count, and more research is needed to confirm their effectiveness and safety. Additionally, some herbs may interact with other medications and can have side effects, so it’s important to consult with a healthcare professional before taking any herbal remedies.
It’s important to consult a healthcare professional for accurate diagnosis and management of platelet deficiency. It’s also important to follow the recommended treatment and lifestyle changes as advised by the healthcare professional to improve platelet count.
KEYWORDS: Platelet count, Thrombocytopenia, Low platelet count, High platelet count, Platelet disorders, Blood clotting, Complete blood count (CBC), Platelets function, Platelets deficiency, Platelets recovery, Platelets count symptoms, Platelets count treatment, Platelets count herbal remedies, Platelets count and disease, Platelets count and diet, pregnancy, alcohol, Platelets count and toxins, medications, vitamin deficiency, autoimmune disorders, bone marrow disorders, Platelets count and infections
REFERENCES:
https://www.academia.edu/download/75850216/pbc.2197820211206-32076-126hmb1.pdf
https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/pdfdirect/10.1111/j.1751-553X.2007.00909.x

Pingback: TYPHOID FEVER-SYMPTOMS AND CURE!! - Life Biologs
Pingback: WHAT IS ECZEMA CURE? - Life Biologs