FOLLOW YOUR HEART BUT TAKE YOUR BRAIN WITH YOU…

The heart is a vital organ located in the chest that is responsible for pumping blood throughout the body. The heart has four chambers: the left and right atria, and the left and right ventricles. The atria are the upper chambers of the heart, and the ventricles are the lower chambers.Hheart has an intricate network of blood vessels, including the arteries and veins, which carry oxygen-rich and oxygen-poor blood to and from the heart. The heart has its blood supply, which is provided by the coronary arteries. The heart has an electrical system that coordinates the contraction of the heart muscle, which pumps blood. This electrical activity can be monitored through an electrocardiogram (ECG), which records the electrical activity of the heart.
The heart is essential for maintaining the circulation of blood throughout the body. It pumps oxygen-rich blood to the body’s tissues and organs and removes waste products from the body. Overall, the heart is a vital organ that plays a central role in maintaining the body’s overall health and well-being. It is important to take care of the heart through a healthy lifestyle, including a healthy diet, regular physical activity, and avoiding tobacco and excessive alcohol consumption.
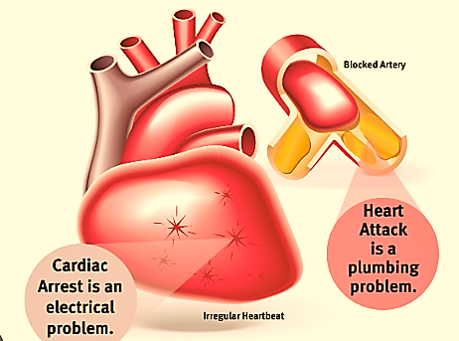
CARDIAC ARREST OR HEART ATTACK
It is a medical emergency that occurs when the heart suddenly stops beating. It is a life-threatening condition that requires immediate medical attention. A heart attack, also known as a myocardial infarction, occurs when the blood flow to the heart is blocked, causing damage to the heart muscle. A heart attack is also a medical emergency that requires immediate medical attention.
Symptoms of cardiac arrest and heart attack may include:
- Chest pain or discomfort
- Shortness of breath
- Nausea
- Sweating
- Lightheadedness
- Fatigue
If you suspect that you or someone else is experiencing cardiac arrest or a heart attack, it is important to call for emergency medical assistance immediately. Cardiac arrest and heart attacks are treated with medications, procedures, and lifestyle changes to help restore normal heart function and prevent future cardiac events. Overall, cardiac arrest and heart attacks are serious medical emergencies that require immediate medical attention. It is important to seek medical care as soon as possible to improve the chances of a favorable outcome.
SIGNS AND SYMPTOMS THAT LEAD TO CARDIAC ARREST WITH TIME
It is a medical emergency that occurs when the heart suddenly stops beating. It is a life-threatening condition that requires immediate medical attention. Some signs and symptoms that may lead to cardiac arrest over time include:
Chest pain or discomfort:
Chest pain or discomfort, particularly during physical activity, can be a sign of a heart attack or other cardiac issues.
Shortness of breath:
Difficulty breathing or shortness of breath, particularly during physical activity, can be a sign of a cardiac problem.
Fatigue:
Persistent fatigue or tiredness, particularly during physical activity, can be a sign of a cardiac issue.
Swelling:
Swelling in the feet, ankles, or legs can be a sign of a cardiac issue, particularly if it is accompanied by shortness of breath or difficulty breathing.
Irregular heartbeat:
An irregular heartbeat or palpitations can be a sign of a cardiac issue.
Dizziness or lightheadedness:
Dizziness or lightheadedness, particularly during physical activity, can be a sign of a cardiac issue.
If you experience any of these signs or symptoms, it is important to consult with a healthcare provider to determine the underlying cause and develop a treatment plan. It is also important to seek immediate medical attention if you experience any of these symptoms in combination with chest pain or discomfort.
ADVICE FOR HYPERTENSION PATIENTS TO SECURE FROM CARDIAC ARREST
Hypertension, or high blood pressure, is a risk factor for cardiac arrest, as it can increase the strain on the heart and blood vessels. To help secure from cardiac arrest, here are some pieces of advice that a healthcare provider may give to a hypertension patient:
Take medications as prescribed:
If you have hypertension, it is important to take your blood pressure medications as prescribed by your healthcare provider. These medications can help lower your blood pressure and reduce your risk of cardiac arrest.
Follow a healthy lifestyle:
Maintaining a healthy lifestyle can help lower your blood pressure and reduce your risk of cardiac arrest. This may include eating a healthy diet, getting regular physical activity, avoiding tobacco and excessive alcohol consumption, and managing stress.
Monitor your blood pressure:
It is important to monitor your blood pressure regularly to ensure that it is under control. You can do this at home with a home blood pressure monitor or by visiting your healthcare provider.
Know the warning signs of cardiac arrest:
It is important to be aware of the signs and symptoms of cardiac arrest and to seek medical attention immediately if you experience any of them. These may include chest pain or discomfort, shortness of breath, nausea, sweating, lightheadedness, or fatigue.
Stay up to date with your healthcare:
It is important to stay up to date with your healthcare and to follow your healthcare provider’s recommendations for managing your hypertension. This may include regular check-ups and blood pressure monitoring.
Overall, hypertension patients need to take steps to lower their blood pressure and reduce their risk of cardiac arrest. Working closely with a healthcare provider and following their recommendations can help lower your risk of cardiac arrest and improve your overall health.
TYPES OF CARDIAC ARREST AND FIRST AID
There are two main types of cardiac arrest: ventricular fibrillation (VF) and pulseless ventricular tachycardia (VT).
Ventricular fibrillation (VF) is a type of cardiac arrest that is caused by abnormal electrical activity in the heart. It results in the heart’s ventricles quivering instead of contracting effectively, which can lead to a lack of blood flow to the body. VF is often treated with a defibrillator, which can help restore the heart’s normal rhythm.
Pulseless ventricular tachycardia (VT) is a type of cardiac arrest that is characterized by a rapid and irregular heartbeat in the ventricles. It can lead to a lack of blood flow to the body and is often treated with medications or a defibrillator.
First aid for cardiac arrest involves immediate treatment to restore normal heart rhythm and blood flow to the body. The first step in treating cardiac arrest is to call for emergency medical assistance. While waiting for emergency responders to arrive, the following steps can be taken to provide first aid for cardiac arrest:
Check for signs of life:
Check for signs of life by looking for breathing and a pulse. If there is no pulse and the person is not breathing, start CPR immediately.
Administer CPR:
If the person is not breathing and has no pulse, start CPR by placing your hands on the person’s chest and compressing at a rate of 100-120 times per minute. If you are not trained in CPR, wait for emergency responders to arrive.
Use an automated external defibrillator (AED):
If an AED is available, follow the instructions to attach the pads to the person’s chest and use the AED to deliver a shock.
Overall, cardiac arrest is a medical emergency that requires immediate treatment to restore normal heart function and blood flow to the body. Providing first aid and calling for emergency medical assistance can help improve the chances of a favorable outcome.
FIRST AID GUIDELINES AT HOME IN CASE OF CARDIAC ARREST
Cardiac arrest is a medical emergency that requires immediate treatment to restore normal heart function and blood flow to the body. If someone experiences cardiac arrest at home, it is important to take immediate action to provide first aid and call for emergency medical assistance. Here are some guidelines for providing first aid for cardiac arrest at home:
Call for emergency medical assistance:
The first step in treating cardiac arrest is to call for emergency medical assistance. Dial 911 or your local emergency number and provide the operator with the location and the person’s condition.
Check for signs of life:
Check for signs of life by looking for breathing and a pulse. If there is no pulse and the person is not breathing, start CPR immediately.
Administer CPR:
If the person is not breathing and has no pulse, start CPR by placing your hands on the person’s chest and compressing at a rate of 100-120 times per minute. If you are not trained in CPR, wait for emergency responders to arrive.
Use an automated external defibrillator (AED):
If an AED is available, follow the instructions to attach the pads to the person’s chest and use the AED to deliver a shock.
Wait for emergency responders to arrive:
Continue CPR and use the AED as directed until emergency responders arrive and take over care.
Overall, it is important to take immediate action and call for emergency medical assistance if someone experiences cardiac arrest at home. Providing first aid and using an AED, if available, can help improve the chances of a favorable outcome. It is also important to seek medical care as soon as possible to address the underlying cause of cardiac arrest and prevent future cardiac events.
HOME REMEDIES FOR A CARDIAC PATIENT
While home remedies may provide some relief for certain cardiac issues, it is important to note that they should not be used as a replacement for medical treatment. It is important for cardiac patients to follow the treatment plan prescribed by their healthcare provider and to seek medical care as needed.
Here are some home remedies that may be helpful for a cardiac patient:
Exercise:
Regular physical activity can help improve heart function and reduce the risk of cardiovascular disease. It is important to consult with a healthcare provider before starting an exercise program.
Eat a healthy diet:
A healthy diet that is low in salt, saturated fat, and added sugars can help lower blood pressure and improve heart health. Foods that are high in fiber, fruits, vegetables, and whole grains are particularly beneficial.
Manage stress:
Chronic stress can increase the risk of heart disease. It is important to find healthy ways to manage stress, such as through meditation, yoga, or exercise.
Get enough sleep:
Getting enough sleep is important for overall health, including heart health. It is recommended to aim for 7-9 hours of sleep per night.
Quit smoking:
Smoking is a major risk factor for heart disease. Quitting smoking can help improve heart health and reduce the risk of cardiovascular disease.
Overall, it is important for cardiac patients to follow the treatment plan prescribed by their healthcare provider and to seek medical care as needed. In addition, making lifestyle changes such as eating a healthy diet, getting regular physical activity, managing stress, and getting enough sleep can help improve heart health.
FIRST AID GUIDELINES AT HOME IN CASE OF CARDIAC ARREST
Cardiac arrest is a medical emergency that requires immediate treatment to restore normal heart function and blood flow to the body. If someone experiences cardiac arrest at home, it is important to take immediate action to provide first aid and call for emergency medical assistance. Here are some guidelines for providing first aid for cardiac arrest at home:
Call for emergency medical assistance:
The first step in treating cardiac arrest is to call for emergency medical assistance. Dial 911 or your local emergency number and provide the operator with the location and the person’s condition.
Check for signs of life:
Check for signs of life by looking for breathing and a pulse. If there is no pulse and the person is not breathing, start CPR immediately.
Administer CPR:
If the person is not breathing and has no pulse, start CPR by placing your hands on the person’s chest and compressing at a rate of 100-120 times per minute. If you are not trained in CPR, wait for emergency responders to arrive.
Use an automated external defibrillator (AED):
If an AED is available, follow the instructions to attach the pads to the person’s chest and use the AED to deliver a shock.
Wait for emergency responders to arrive:
Continue CPR and use the AED as directed until emergency responders arrive and take over care.
Overall, it is important to take immediate action and call for emergency medical assistance if someone experiences cardiac arrest at home. Providing first aid and using an AED, if available, can help improve the chances of a favorable outcome. It is also important to seek medical care as soon as possible to address the underlying cause of cardiac arrest and prevent future cardiac events.
s, Aorta, Aortic valve, Angioplasty, Atrial fibrillation, Cardiologist, Congenital, Coronary Arteries, Coronary artery disease
REFERENCES:
- Bernard, S. A., Gray, T. W., Buist, M. D., Jones, B. M., Silvester, W., Gutteridge, G., & Smith, K. (2002). Treatment of comatose survivors of out-of-hospital cardiac arrest with induced hypothermia. New England journal of medicine, 346(8), 557-563.
- Moulaert, V. R., Verbunt, J. A., van Heugten, C. M., & Wade, D. T. (2009). Cognitive impairments in survivors of out-of-hospital cardiac arrest: a systematic review. Resuscitation, 80(3), 297-305.

Pingback: YOU’RE THYROID HEALTH WITH TREATMENT!! - Life Biologs